CTargetAddress
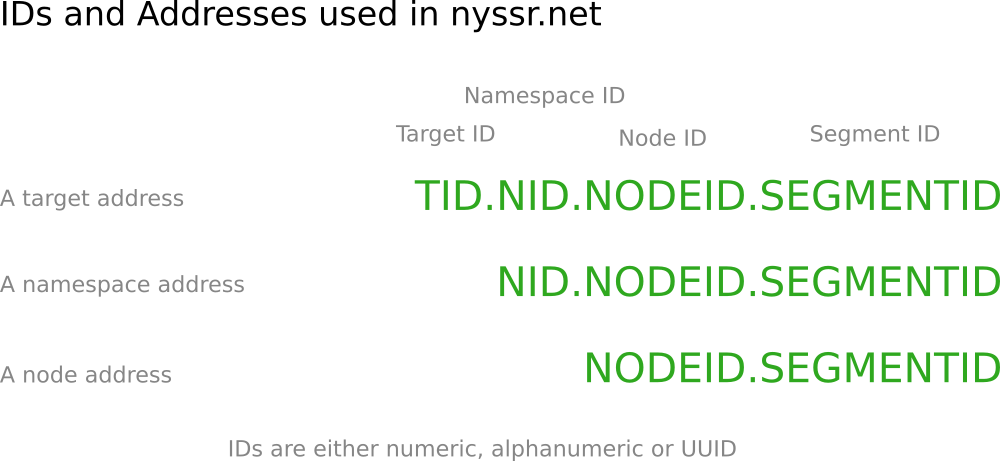
The target address is assigned to a target when it has been successfully registered with the target registry. The target address is composed of a target ID (unique for a namespace) and the namespace address.
Constructors
First follows a constructor with the passing of all four components:
public CTargetAddress(@NotNull final IId aTargetID, @NotNull final IId aNamespaceID, @NotNull final CNodeId aNodeId, @NotNull final CSegmentId aSegmentId);
The SegmentId remains empty here. An empty NodeId or SegmentId is equivalent to specifying a local ID.
public CTargetAddress(@NotNull final IId aTargetID, @NotNull final IId aNamespaceID, @NotNull final CNodeId aNodeId);
The node address consists of a node ID and a segment ID.
public CTargetAddress(@NotNull final IId aTargetID, @NotNull final IId aNamespaceID, @NotNull final CNodeAddress aNodeAddress);
The node ID and the segment ID remain empty, so they are local.
public CTargetAddress(@NotNull final IId aTargetID, @NotNull final IId aNamespaceID);
The namespace address consists of namespace ID, node ID and segment ID.
public CTargetAddress(@NotNull final IId aTargetID, @NotNull final CNamespaceAddress aNamespaceAddress)
Factory Methods
The target address can also be created from a string. The structure of the string is described in the picture above.
@Nullable public static CTargetAddress fromString(@Nullable final String aStr);
Similarly, the target address can also be created from the components (Integer, String, UUID) of the components:
@NotNull
public static CTargetAddress fromObject(@Nullable final Object aTargetID,
@Nullable final Object aNamespaceID,
@Nullable final Object aNodeId);
A random address can be created for test purposes.
@NotNull public static CTargetAddress random();
Creating arrays of random target addresses can be done with this method.
The size of the array can be specified, as well as whether the array may contain null values.
@Nullable
public static CTargetAddress[] randomArray(final int aSize,
final boolean aWithNullValues);
An empty address is created in this way:
@NotNull public static CTargetAddress getInvalidAddress();
Stream I/O
This method writes a target address to a stream.
The target address can also be null.
public static void toStream(@NotNull final DataOutput aStream,
@Nullable final CTargetAddress aValue) throws IOException;
This can be used to read a target address from a DataInput stream.
The read address can be null.
@Nullable public static CTargetAddress fromStream(@NotNull final DataInput aStream) throws IOException;
String I/O
The target address can be converted into a string from which the address can be read again without loss. There is a static and a non-static variant.
@NotNull public static String valueToString(@Nullable final CTargetAddress aValue); @NotNull public String valueToString()
The factory method discussed above is used for reading.
@Nullable public static CTargetAddress fromString(@Nullable final String aStr);
Getter
The components can be fetched via getter methods.
@NotNull public IId getTID(); @NotNull public IId getNID(); @NotNull public CNodeId getNodeId(); @NotNull public CSegmentId getSegmentId(); @NotNull public CNodeAddress getNodeAddress(); @NotNull public CNamespaceAddress getNamespaceAddress();
Verifications
Check whether a target address contains a valid target ID:
public static boolean hasValidTID(@Nullable final CTargetAddress aAddress);
This method does the same thing.
public boolean isValid();
Checks if the target address corresponds to the local node.
public boolean isLocalNode();
Convenience methods
Since a target address is immutable, there are a few methods to create a new address with modified components.
@NotNull public CTargetAddress changeTID(@Nullable final IId aTargetID); @NotNull public CTargetAddress changeNID(@Nullable final IId aNamespaceID); @NotNull public CTargetAddress changeNodeId(@Nullable final CNodeId aNodeId); @NotNull public CTargetAddress changeNodeAddress(@Nullable final CNodeAddress aNode);
This method replaces empty namespaces ids, node ids and segment ids with the respective local ID.
It returns null if nothing has changed.
@Nullable public CTargetAddress getCompletedAddress();
Comparison
The method checks if the target id matches the one in the address.
public boolean match(@Nullable final IId aTID);
The method checks if the namespace id matches the one in the address.
public boolean matchNid(@Nullable final IId aNID);
This method also checks for consistency:
public boolean match(@Nullable final IId aTID, @Nullable final IId aNID, @Nullable final CNodeId aNodeId, @Nullable final CSegmentId aSegmentId);
Notice
CTargetAddress supports the equals and hashCode methods.